Eleanor Roosevelt's Life

1884
October 11: Eleanor Roosevelt is born in New York City.
1892
Elliott Roosevelt, Eleanor's father, is confined to a mental asylum; Eleanor's mother, Anna Hall Roosevelt, dies of diphtheria.
1894
August 13: Elliott Roosevelt dies of alcoholism.
1899
Eleanor enrolls at Allenswood School in England.

1901
President McKinley is assassinated six months after his second inauguration; Theodore "Teddy" Roosevelt, Eleanor's uncle, assumes the presidency.
1902
Eleanor leaves Allenswood and makes her society debut at the Waldorf-Astoria Hotel in New York City.
1903
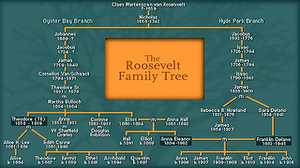
Eleanor becomes engaged to Franklin Delano Roosevelt, her fifth cousin once removed. She enrolls in the Junior League of New York where she teaches calisthenics and dancing to immigrants. She joins the Consumers' League and investigates working conditions in the garment districts.
1905
March 17: Eleanor marries Franklin D. Roosevelt in New York.

1906
May 3: Eleanor gives birth to her first child, Anna.
1907
December 23: Eleanor gives birth to her second child, James.
1909
March 18: Eleanor gives birth to her third child, Franklin, Jr. He dies of influenza soon after.
1910
September 23: Eleanor has her fourth child, Elliott.

1912
Eleanor attends her first Democratic Party Convention.
1913
FDR becomes Assistant Secretary of the Navy. Eleanor hires Lucy Mercer as her social secretary.
1914
August 17: Eleanor gives birth to her fifth child, Franklin Jr. World War I breaks out in Europe.
1916
March 17: Eleanor gives birth to John, her sixth and last child.
1917
The United States enters World War I.
1918
Eleanor learns of the affair between her husband and Lucy Mercer. The Treaty of Versailles is ratified; The House of Representatives passes the amendment to grant women suffrage.
1919
Eleanor volunteers at St. Elizabeth Hospital to visit World War I veterans; She volunteers at the International Congress of Working Women in Washington. Congress passes the Eighteenth Amendment declaring Prohibition.
1920
Eleanor travels with Franklin on his campaign trail for the vice presidency; She becomes friends with Louis Howe; She joins the League of Women Voters.
Congress passes the Nineteenth Amendment granting women the right to vote.
1921
Franklin becomes paralyzed from polio.
1922
Eleanor becomes a member of the Women's Trade Union League; She joins the Women's Division of the Democratic State Committee and meets Marion Dickerman and Nancy Cook.
1924
Congress passes Immigration Acts designed to stem the flow of Southern and Eastern European immigrants into the United States; The Kellogg-Briand Pact (Pact of Paris) which "outlaws war" passes Congress with overwhelming support.
1925
Franklin builds Val-Kill Estate for Eleanor in Hyde Park; Eleanor founds the Val-Kill furniture factory along with Dickerman and Cook.
1926
Eleanor, Dickerman and Cook purchase Todhunter School, a girls seminary in New York, where Eleanor teaches history and government.
1927
Eleanor meets Mary McLeod Bethune, president of Bethune-Cookman college
1928
The Democratic National Committee appoints Eleanor director of Bureau of Women's Activities; FDR is elected as governor of New York.
President Herbert Hoover declares that the United States is nearer than ever to a "final triumph over poverty."
1929
October 24: The New York Stock Exchange crashes.
1932
Veterans march to the White House as the "Bonus Army"; Franklin D. Roosevelt is elected president of the United States.
1933
March 6: Eleanor becomes the first wife of a president to hold all-female press conferences; She assists with the Arthurdale homestead project for coal miners in West Virginia. President Franklin D. Roosevelt implements the New Deal. The Dust-Bowl devastates the Midwest.
1934
Eleanor assists with the formation of the National Youth Administration; She coordinates meeting between FDR and NAACP leader Walter White to discuss anti-lynching legislation.
1935
Eleanor coordinates a meeting with FDR, James Farley, head of the Democratic National Committee, and Molly Dewson, head of the Women's Division of the DNC, to discuss the role of women in political elections; She begins publishing the syndicated column, "My Day."
1936
FDR runs for and wins re-election.
1939
Eleanor defies segregation laws when she sits between whites and blacks at the Southern Conference for Human Welfare in Birmingham, Alabama; She arranges for Marian Anderson to sing at the Lincoln Memorial on Easter Sunday.
Hitler invades Poland and war breaks out in Europe.
1940
July 17: Eleanor makes an impromptu speech at the Democratic National Convention which helps FDR to win an unprecedented third term in office.
1941
December 7: Japan bombs Pearl Harbor and the U.S. enters the war in Europe.
1943
Eleanor tours the South Pacific to boost the soldiers' morale. The Detroit Race Riot occurs as a result of mounting tensions between black and white residents of the city.

1945
Eleanor influences the Army Nurse Corps to open its membership to black women; She joins the NAACP board of directors.
April 12: Franklin Delano Roosevelt dies while convalescing in Warm Springs, Georgia.
September 2: Japan surrenders to the Allies, World War II ends.
1946
Eleanor is elected as head of the United Nations Human Rights Commission; She begins to draft the Declaration of Human Rights; She initiates the creation of Americans for Democratic Action, a group which focuses on domestic social reform and resistance against Russia and the developing Cold War.
1948
Eleanor speaks on "The Struggles for the Rights of Man" at the Sorbonne during a meeting of the United Nations General Assembly in Paris; She threatens her resignation from the UN if Truman does not recognize the newly formed state of Israel; She joins her daughter, Anna, for a radio discussion program on ABC.
December 10: The Human Rights Declaration is passed by the United Nations.

1950
Eleanor joins her son, Elliott, for a television and radio show on NBC.
1952
Eleanor resigns from the United Nations; She campaigns for Adlai Stevenson for the presidency.
1953
The Women's Division of the Democratic National Committee is abolished and its members are integrated into the existing Democratic party structure.
1954
The Brown v. Board of Education decision outlaws segregation in public schools.
1957
Eleanor visits the Soviet Union as a representative of the New York Post and meets Nikita Khrushchev.
The Civil Rights Act is passed by Congress.

1958
Eleanor speaks at a civil rights workshop at Highlander Folk School in Tennessee despite threats from the Ku Klux Klan.
1960
Eleanor supports John F. Kennedy's presidential campaign.
1961
Kennedy re-appoints Eleanor to the United Nations and appoints her as chair of the President's Commission on the Status of Women.
1962
Eleanor spearheads an ad hoc Commission of Inquiry into the Administration of Justice in the Freedom Struggle; She monitors and reports on the efforts and progress of the fight for civil rights in the United States.
November 7: Eleanor dies at the age of seventy-eight of tuberculosis.