M.D. Specialties
Do you know what an otolaryngologist is? Test yourself. Is an otolaryngologist
With more than 20 accredited medical specialties in the United States, it's easy to confuse pediatrics with podiatry or forget altogether what an otolaryngologist does. Here's a chance to brush up on your knowledge of medical specialties and find out if you answered our mini-quiz correctly. Click on each specialty for a description. [+] descriptionAnesthesiology While many of us associate anesthesiologists with operations, these doctors also play a central role in the care of patients outside the operating room. Both before and after surgery as well as during operations, anesthesiologists closely monitor their patients' circulation, respiration, blood-gas levels, and pain in order to facilitate a successful surgery and recovery. Because anesthesiologists must tailor-make an anesthetic program to suit the specific condition of each patient, their specialty is one of the broadest in medicine, requiring knowledge of all aspects of clinical medicine, especially respiratory and circulatory physiology, the devices used to support and monitor these systems, and the drugs that act upon them. Some anesthesiologists specialize in pain management or intensive care. [+] descriptionAllergy and Immunology Doctors specializing in the fields of allergy and immunology focus primarily on treating patients under siege by their own immune systems. Whether their patients suffer from a minor rash brought on by exposure to an allergen in nature or an auto-immune disease such as multiple sclerosis or lupus, allergists and immunologists must be careful diagnosticians, analyzing tests and gathering specific information about their patients' environments in order to prescribe the best mode of treatment or prevention. [+] descriptionCardiology Cardiologists treat patients with conditions of the heart, blood vessels, and circulation. They often serve as consultants to other physicians with patients whose illnesses involve the circulatory system. To evaluate a patient's condition, cardiologists use tests such as the electrocardiogram (EKG), which graphically records electric currents generated by the heart. Some cardiologists specialize in procedures such as cardiac catheterization. [+] descriptionDermatology Dermatologists diagnose and treat medical disorders that cause problems with the skin, the most common of which are acne, psoriasis, and eczema. Though dermatologists usually treat their patients using prescription drugs, they also perform outpatient procedures, from mole removals to chemical peels. [+] descriptionEmergency Medicine Made famous by the television blockbuster "E.R.," emergency medicine often requires a doctor's split-second, life-or-death decision under conditions of extreme pressure. An emergency physician's primary role is to quickly recognize, evaluate, and stabilize patients who come into the emergency department. Because the conditions of patients in the emergency room run the gamut, these doctors must be well-versed in almost every area of medicine, at least enough to preliminarily care for a patient and call upon the correct specialist to administer further care. (For an inside look at this specialty, see One Night in an E.R..) [+] descriptionEndocrinology Endocrinologists commonly treat patients with thyroid disorders, diabetes, and eating disorders in order to bring the body's chemistry, cellular functions, and metabolism under control. [+] descriptionFamily Practice Family practitioners are responsible for the total care of their patients, old and young, following their health over a number of years and coordinating their care with specialists when needed. With their vast range of medical knowledge, family practitioners are generally the first stop for most patients seeking medical advice, whether for a sore throat or a more serious medical concern. [+] descriptionGeneral Surgery General surgeons have broad-based experience in anatomy, physiology, wound healing, shock and resuscitation, and intensive-care medicine. They perform surgery to treat conditions in the abdomen, breasts, head and neck, and vascular system. They repair hernias and remove appendixes and cysts. Though many of the procedures that general surgeons perform may also be done by surgical specialists, general surgeons are often called in to perform surgeries in conjunction with a specialist or after a specialist has already diagnosed a patient and ordered a surgical treatment. [+] descriptionGastroenterology Gastroenterologists care for patients who have conditions of the esophagus, stomach, gall bladder, liver, pancreas, and intestines. In addition to performing procedures related to conditions in these organs and providing preventive screening for diseases such as colon cancer, gastroenterologists also treat patients with common disorders such as heartburn and ulcers on an outpatient basis. [+] descriptionHematology Hematology is the medical field concerned with the treatment of blood and blood-tissue disorders. Using special methods to examine the structure of a patient's blood, hematologists diagnose and treat a range of blood-related diseases such as leukemia, hemophilia, and myeloma. Hematologists often work in conjunction with other specialists to care for a patient with a disease of the blood. [+] descriptionInternal Medicine Internal medicine is the specialty that deals with the general medical treatment of adults. Rather than focusing on a particular organ or body system, internal-medicine physicians are concerned with the total body health of their patients. Internists have wide-ranging medical knowledge and are capable of treating a host of medical problems, from minor to severe. Many internists choose to focus their expertise to include special care in certain areas, such as geriatrics. [+] descriptionNeurology Neurologists specialize in the treatment of all aspects of nervous-system health, from migraine headaches to stroke and epilepsy. Neurologists work closely with psychiatrists when dealing with neurological disorders that affect emotional or mental functioning. [+] descriptionObstetrics and Gynecology Obstetricians and gynecologists focus on the health of the female reproductive system. Although they are not separate specialties, doctors often choose to spend more time in either obstetrics or gynecology. Technically, however, obstetricians care for women during pregnancy and through delivery, while gynecologists diagnose, treat, and screen for disorders and diseases of the female reproductive system. Gynecologists administer "Pap" smears to test for reproductive cancers, prescribe various methods of birth control, perform abortions, treat urinary tract illnesses, and examine breasts for irregularities. [+] descriptionOphthalmology Ophthalmologists prescribe glasses and perform routine checks for diseases of the eye such as glaucoma. They also conduct surgeries on the eye to remove cataracts, correct various eye disorders, and transplant corneas, among other procedures. [+] descriptionOccupational Medicine The field of occupational medicine focuses on the preservation of health and prevention and treatment of workplace-related disease and injury. Occupational-medicine specialists must be well versed in the effects of radiation, in toxicology, orthopedics, and environmental hazards. They work both in and out of their offices, treating patients who have been injured in the workplace and surveying work environments to ensure that they are safe. Specialists in occupational medicine also advise employees and employers on how to work more safely, both in terms of handling equipment and dealing with psychological and environmental stresses. [+] descriptionOncology Oncologists examine, diagnose, and treat patients with cancer. Oncologists often work in close conjunction with surgeons and radiologists in order to treat patients with cancer. [+] descriptionOrthopedic Surgery Orthopedic surgeons treat patients with medical conditions of the musculoskeletal system. They handle broken and fractured limbs, perform surgeries to correct sports-related injuries, do joint replacements and see patients with congenital skeletal malformations and degenerative diseases such as osteoporosis. In their treatment of patients, orthopedic surgeons use the techniques of physical and rehabilitation therapies in addition to performing surgery and prescribing medicine. [+] descriptionOtolaryngology Otolaryngologists are otherwise known as ear, nose, and throat (ENT) doctors. They treat patients with a range of problems in these areas of the upper body, from ear infections to sinus problems and disorders of the larynx, or voice box. Otolaryngologists perform surgery and, because they regularly operate in conspicuous locations on the face and neck, are often trained in the art of plastic and reconstructive surgery. [+] descriptionPathology Patients rarely come into direct contact with pathologists, since their work is primarily lab-related, but the discreet role of pathologists in the daily administration of medicine is extremely vital. Pathologists examine tissues and conduct lab tests, confer with clinicians about which tests to order and which treatments to prescribe, and are crucial in helping to determine the correct diagnosis. [+] descriptionPediatrics Pediatricians care for the physical health of children and closely monitor their development from birth to adolescence. They not only provide primary and preventive health care for children, but they also treat chronic and acute pediatric diseases, such as diabetes and epilepsy, and help to educate parents on how to maintain the health of their children at home in their day-to-day lives. [+] descriptionPlastic Surgery Plastic surgeons perform operations to restore or correct their patients' appearance. Whether the goal of a procedure is to beautify a nose, correct a physical birth defect, repair facial structures after serious trauma, or reconstruct parts of the body ravaged by cancer, plastic surgeons use meticulous and often artful methods of surgery to help their patients feel better about their appearance and function better in their everyday lives. [+] descriptionPsychiatry Psychiatrists treat mental, addictive, and emotional disorders, medically managing patients with drug treatments and helping patients and their families cope with problems and stress. Often psychiatrists work in conjunction with a patient's primary-care physician to help treat a range of disorders, such as depression, anxiety, psychosis, and substance abuse. [+] descriptionPublic Health and General Preventative Medicine Public-health specialists, though they may see patients, are usually not involved with day-to-day clinical care. Overall, doctors in this specialty serve as advocates for community health and address the public and public officials on matters of health likely to affect us all, such as diet, stress, infectious diseases, and environmental contamination. Public-health and general-preventative-medicine specialists are often involved in research and educational activities that increase public awareness of health risks. [+] descriptionPulmonology Pulmonologists treat patients with lung disorders and diseases, including asthma, chronic bronchitis, and lung cancer. Pulmonologists often work in such diverse areas as occupational medicine, intensive-care units, and direct respiratory-therapy departments. [+] descriptionRadiology Two fields fall under the umbrella of radiology: diagnostic radiology and oncological radiology. Diagnostic radiologists administer, read, and interpret CT scans, ultrasounds, magnetic resonance images, and X-rays, all of which are diagnostic tools that help doctors assess and monitor a range of medical conditions, from sprained ankles to brain tumors. Some radiologists perform special procedures that can break up blood clots and turn off misfiring nerve endings. Radiation oncologists, now a separate subspecialty, see patients after they have been diagnosed with a condition such as cancer for which radiation therapy is the prescribed course of treatment. Radiation oncologists use various forms of radioactive energy to penetrate a patient's body and eradicate tumors. [+] descriptionThoracic Surgery Thoracic surgery, also called cardiothoracic surgery, involves surgery to the chest. Thoracic surgeons are trained to diagnose and operate on conditions of the heart, lungs, and esophagus. Thoracic surgeons often consult with pulmonologists and cardiologists in their treatment of patients. [+] descriptionUrology Urologists diagnose and treat illnesses and disorders of the male and female urinary tract and male reproductive organs. Though urologists treat female patients with urinary disorders, many of a urologist's patients are men with sexual dysfunction or cancers of the kidneys, bladder, prostate, or testicles. Urologists perform surgical procedures, such as vasectomies, prostatectomies, or operations to remove bladder cancers. |
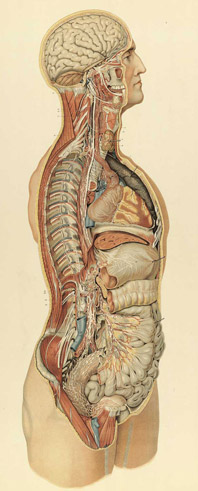
A drawing from the late-19th-century medical textbook entitled Anatomie normale du corps humain: atlas iconographique de XVI planches (Normal anatomy of the human body: an iconographic atlas of 16 plates), written by Sigismond Laskowski, illustrated by Sigismond Balicki, and published in Geneva in 1894 |
|
This feature originally appeared on the NOVA website in 2001, when Sydney Rose was an intern and Lexi Krock the editorial assistant at NOVA Online. Sydney Rose later went on to study medicine at Weill Cornell Medical College in Manhattan. As of April 2009, she was still deciding on her specialty. Doctors' Diaries Home | Send Feedback | Image Credits | Support NOVA |
© | Created February 2009 |
|
|
|
