 |
 |
 |
 |
Watch The Program: Teachers
This hour-long program is divided into eight chapters. Choose any chapter below and select QuickTime or Real Video to begin viewing. If you experience difficulty viewing, it may be due to high demand. We regret this, and suggest you try back at another time. Due to rights restrictions this program is not available for downloading. This program is rated TV-14,S. Viewer discretion is advised.
Feedback |
Technical Help |
Program Credits |
Program Transcript
Advanced options |
Watch other NOVA programs online
|
 |

|
1. Passing on Your DNA
This chapter:
states that human bodies are designed to make babies. points out that human bodies are made up of about 100 trillion cells and
composed of tissues and organs. notes that sexual reproduction allows two individuals to provide DNA to
create new beings that are different from their parents.
running time 09:53
|
|
watch it in
QuickTime |
RealVideo
|
|
 |
|
2. The Egg's Journey
This chapter:
introduces a man and a woman expecting a baby. states that men produce sperm from puberty on, but all of a female's eggs
are made when a fetus. explains ovulation. notes that an egg has all components to start life except DNA from sperm,
and a few hours after being released, the egg will die if it does not join with
a sperm. discusses human sexual chemistry and the physical aspects of it.
running time 06:00
|
|
watch it in
QuickTime |
RealVideo
|
|
 |
|
3. The Sperm's Journey
This chapter:
states that the acidic nature of the vagina kills sperm that don't travel
quickly enough through it. tells that even in healthy men, up to about 60 percent of the sperm are
imperfect. explains that woman's body controls whether or not a healthy sperm
reaches an egg and successfully fertilizes it. states what happens to the cervix during ovulation, describes the sperms'
journey into a fallopian tube, and notes how sperm fertilizes the egg.
running time 05:41
|
|
watch it in
QuickTime |
RealVideo
|
|
 |
|
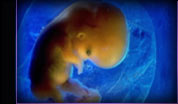
4. The First Two Weeks
This chapter:
states that sperm and egg join to create a viable embryo, but more than
50 percent of all fertilized eggs don't develop. explains that after the sperm enters the egg, meiosis is completed. discusses the process of how the cells, now called a blastocyst, move
toward and attach to the mother's uterine lining.
running time 04:58
|
|
watch it in
QuickTime |
RealVideo
|
|
 |
|
5. The Embryo Takes Shape
This chapter:
explains that when the blastocyst is the size of a poppy seed, cells
organize into an embryo. discusses gastrulation, a process in which three different layers of
cells develop, and different organs develop from each layer. tells that at four and one-half weeks, the embryo is about 1/5 in.
long. summarizes that all organs develop from the same cell with 46
chromosomes, but cells in different organs do not look alike because different
genes are activated in different cell types causing different proteins to be
made.
running time 07:47
|
|
watch it in
QuickTime |
RealVideo
|
|
 |
|
6. Messages in the Genes
This chapter:
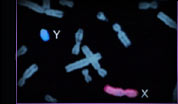
notes that one pair of chromosomes among 23 determine the sex—XX
for female and XY for male. explains that late in the sixth week, a chain of chemical reactions occur
turning on some genes and off others. presents how the journey becomes a fetus. tells that at six months, the fetus is 400 times larger than at two
months.
running time 04:35
|
|
watch it in
QuickTime |
RealVideo
|
|
 |
|
7. Feeding the Growing Fetus
This chapter:
explains that in a growing fetus a few crucial events are still
occurring, including fat being laid down in the brain. describes the role of the placenta.
outlines
how different body organs develop.
running time 06:39
|
|
watch it in
QuickTime |
RealVideo
|
|
 |

|
8. The Third Trimester
This chapter:
notes that by the third trimester, all organ systems are in place. describes how fat is laid down in the brain, and how a fatty covering
called myelin surrounds nerve cells. explains the brain's need for nourishment during the final trimester. shows the birth of the developed fetus, and explains how dangerous human
births were, particularly before C-sections were possible.
running time 07:07
|
|
watch it in
QuickTime |
RealVideo
|
|